In my previous article, I discussed the applications of mobile emergency energy storage vehicles. Now, let’s dive deeper into the internal structure of these mobile battery vehicles. They consist of the following key components:
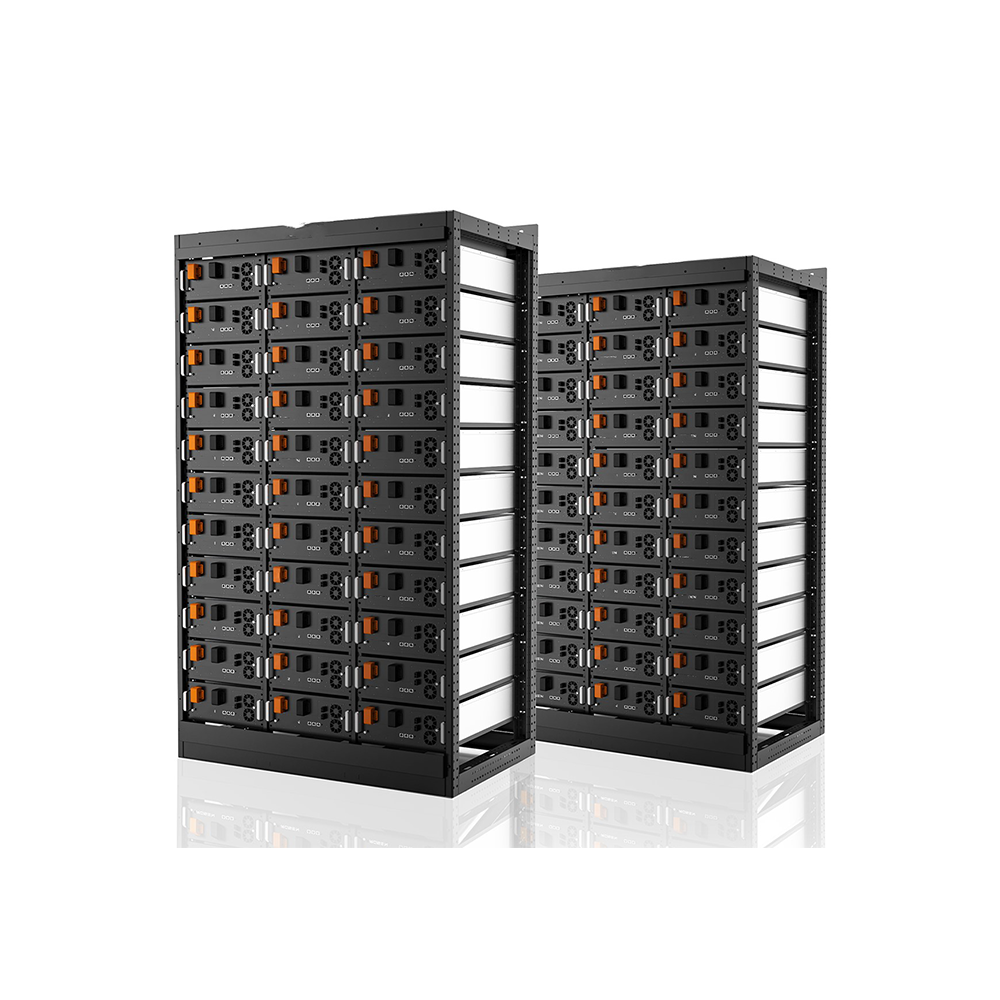

1. Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) Battery System
The LFP Battery System is the core of mobile battery vehicles. It is comprised of multiple battery packs, a high-voltage main control box, and a Power Conversion Systems (PCS) set.
The energy storage component used Lithium Iron Phosphate which has the following characteristics: high energy density, long cycle life, and large charging and discharging rates. Aside from that, it is also safe and eco-friendly. This battery pack is secured into a battery holder using screws and plywood at the front and back.
Another component of the battery system is the BMS or Battery Management System, which is used to monitor the health of energy storage batteries. It is used to intelligently manage and maintain each battery unit, preventing the battery from overcharging and over-discharging which helps extend the battery’s service life. You’ll usually find the BMS as a circuit board or a hardware box.
Finally, another essential component is the Power Conversion Systems (PCS) set. In addition to the bidirectional inverter function, the PCS set can also support the grid, ensuring the stable operation of the grid system. It provides resistance to short-term impact, a smooth power supply, energy storage, and peak shaving.
LFP Battery Systems have many applications including electric vehicles (EVs), peak shaving, frequency modulation, emergency backup power supply, and more.
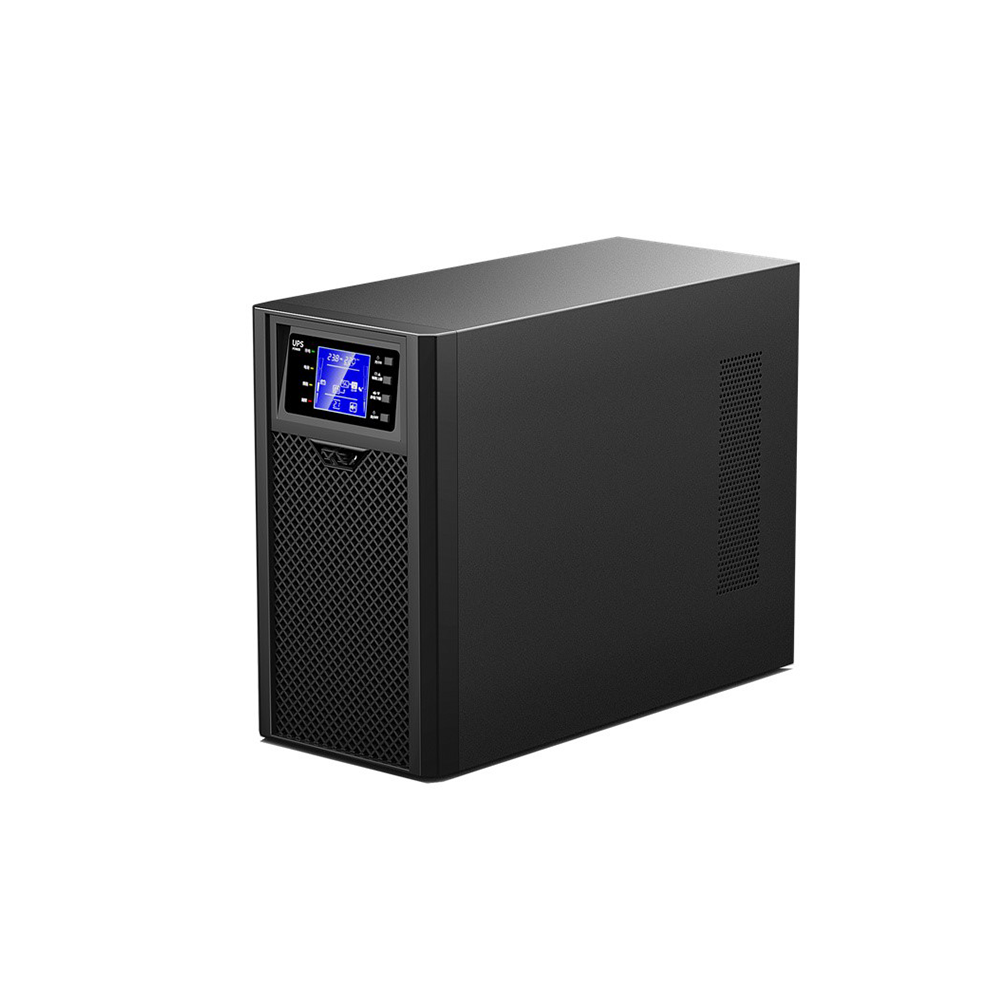

2. Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS)
An Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) is a system device that connects the battery (lead-acid maintenance-free batteries) to the host and converts DC power into commercial power through module circuits such as the host inverter. UPS power serves as a backup power supply during equipment startup.

3. Gyroscope
A gyroscope is a high-performance 3D motion attitude measurement system based on MEMS technology. It has motion sensors such as a three-axis gyroscope and a two-axis accelerometer. It integrates these high-performance sensors and uses a self-developed attitude dynamics core algorithm engine. Combined with a Kalman filter fusion algorithm, a gyroscope provides high-precision, highly dynamic, and real-time compensated three-axis attitude angles—offering flexible selection and configuration of various data types to meet different application scenarios.

4. Infrared Camera
An infrared temperature sensor is essential for the interior monitoring system. This sensor connects to the equipment host through RS485 communication, enabling real-time monitoring of the internal environment.
5. Heat Dissipation System
The primary equipment in the electrical room, the PCS system, utilizes direct exhaust cooling to maintain proper temperature. The battery compartment uses industrial air conditioning to control the temperature.
6. Fire Protection System
Safety is very important, so these vehicles come with special fire extinguishers that use heptafluoropropane (HFC-227ea) gas. Heptafluoropropane is a widely used product known for environmental protection, safety, and economic costs. Heptafluoropropane fire extinguishers are colorless, odorless, and don’t conduct electricity. They are also not very toxic and don’t create any extra pollution.
Its fire-extinguishing mechanism is similar to methylalkane series fire-extinguishing agents. During combustion, the fire-extinguishing agent decomposes thermally, generating fluorine-containing free radicals. These free radicals (H+, OH-, and O2-) react in the gas phase to suppress the chemical reaction during combustion, effectively extinguishing the fire.
7. EMS system
The core Energy Management System, or EMS, is another critical component. The EMS is directly responsible for the control strategy of the energy storage system. This control strategy significantly impacts the battery’s decay rate and cycle life, ultimately affecting the economic viability of the energy storage system. The EMS also monitors for system abnormalities during operation to provide timely and rapid troubleshooting, ensuring equipment protection and overall safety.
These are the essential parts that make up a mobile emergency battery vehicle. Optimal performance and safety rely on the scientific integration of these various systems. If you’re interested in such a solution, send us a message at Charge Ninja.
